Female Vagina
Every woman’s vagina is different – some larger, some smaller, and some may be long or round. Categorizing all the different types and size can be quite challenging.
What is the Female Vagina?
Definition
The vagina is a stretchy, muscular canal that connects the external genitals (the vulva) to the cervix and uterus in females. It serves multiple essential functions, including facilitating sexual intercourse, allowing for menstrual fluid to exit the body, and providing a birth canal during childbirth.
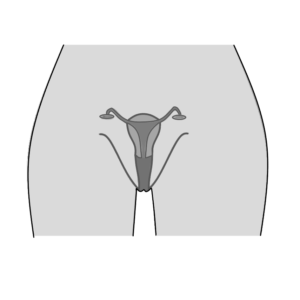
Anatomy of the Vagina
- Location: The vagina is located within the pelvis, positioned between the bladder (anteriorly) and the rectum (posteriorly). It extends from the vaginal opening at the vulva to the cervix of the uterus.
- Structure: The vagina is a fibromuscular tube that can expand and contract. Its walls typically collapse against each other when not aroused but can stretch significantly during sexual arousal or childbirth due to its elastic nature.
- Length: On average, an unaroused vagina measures about 3.5 inches (approximately 9 cm) in depth but can vary based on individual anatomy and factors such as age and hormonal changes.
- Layers: The vaginal wall consists of several layers:
- Mucosa: The innermost layer lined with stratified squamous epithelium that maintains moisture and protects against infections.
- Muscular Layer: Composed of smooth muscle fibers arranged in circular and longitudinal layers, allowing for flexibility and contraction.
- Adventitia: The outermost layer providing structural support, rich in collagen and elastic fibers.
Functions of the Vagina
- Sexual Intercourse: During sexual arousal, blood flow increases to the vaginal walls, causing them to engorge with blood and produce lubrication for comfortable penetration.
- Menstruation: The vagina acts as a passageway for menstrual fluid to exit the body during menstruation.
- Childbirth: During delivery, the vagina expands significantly to allow a baby to pass through from the uterus to outside of the body.
- Sperm Transport: The vagina serves as a receptacle for sperm during intercourse, allowing sperm to travel through it into the cervix and uterus for potential fertilization of an egg.
Health Considerations
Maintaining vaginal health involves regular pelvic exams, practicing safer sex to reduce infection risk, avoiding douching which can disrupt natural flora, and being aware of any changes in discharge or discomfort that may indicate infection or other health issues.
In summary, the vagina is a vital component of female reproductive anatomy, playing crucial roles in sexual function, menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth while also requiring proper care to maintain its health.
Major Parts of the Female Vagina
The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the external genitals to the uterus. Key components include:
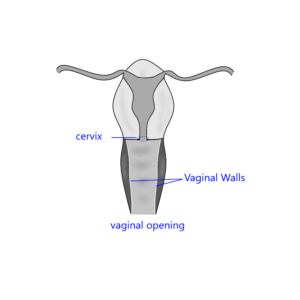
- Vaginal Opening: The entrance to the vagina, located between the urethra and anus.
- Cervix: The lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina, allowing menstrual fluid to exit and sperm to enter.
- Vaginal Walls: Composed of elastic tissue, they can stretch during sexual arousal and childbirth.
- Bartholin’s Glands: Located near the vaginal opening, these glands produce lubrication during arousal.
These parts work together for reproductive functions, sexual pleasure, and childbirth.
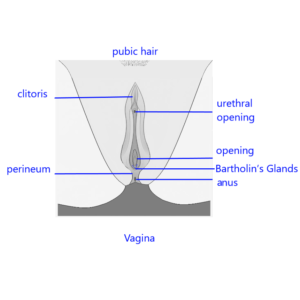
What are sensitive parts of the female vagina ?
The female vagina and surrounding areas contain several sensitive organs and structures that contribute to sexual arousal and pleasure. Here are some of the key sensitive areas:
Clitoris : As mentioned earlier, the clitoris is the most sensitive part of the female anatomy, containing a high concentration of nerve endings. It is primarily responsible for sexual pleasure.
Vaginal Walls : The walls of the vagina have nerve endings that can respond to touch and pressure. While the vaginal canal itself is less sensitive than the clitoris, stimulation of the vaginal walls can still contribute to sexual arousal.
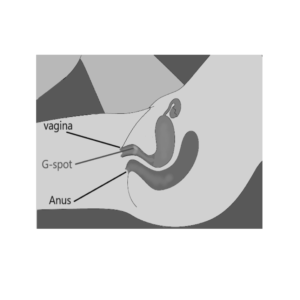
G-Spot : The G-spot, or Grafenberg spot, is an area located a few inches inside the vagina on the anterior (front) wall. Some women report that stimulation of this area can lead to intense pleasure and even orgasm.
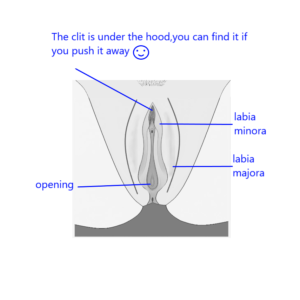
Labia : The labia majora (outer lips) and labia minora (inner lips) are sensitive areas that can respond to touch. They also contain nerve endings that can enhance sexual arousal.
How to protect vagina from getting hurt during sex ?
To help protect the vagina from discomfort or injury during intercourse, women can consider the following strategies:
- Communication with Partner : Openly discuss preferences, boundaries, and comfort levels with your partner. This can help ensure that both partners are on the same page regarding what feels good and what does not.
- Adequate Foreplay : Engaging in sufficient foreplay can help increase arousal and natural lubrication, making intercourse more comfortable. This can include kissing, touching, and oral sex.
- Use of Lubricants : If natural lubrication is insufficient, using a water-based or silicone-based lubricant can reduce friction and enhance comfort during intercourse.
- Choosing Comfortable Positions : Experimenting with different sexual positions can help find what feels best and is most comfortable. Some positions may allow for better control and less discomfort.
- Taking It Slow : Gradually increasing the intensity and pace of intercourse can help the body adjust and reduce the risk of pain or injury.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises : Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises like Kegels can improve muscle tone and control, potentially enhancing comfort during intercourse.
- Regular Gynecological Check-ups : Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help identify any underlying issues that may contribute to discomfort during intercourse, such as infections or hormonal imbalances.
- Avoiding Irritants : Be mindful of products that may irritate the vaginal area, such as scented soaps, douches, or certain contraceptives. Opt for gentle, unscented products.
- Listening to Your Body : Pay attention to your body’s signals. If something feels painful or uncomfortable, it’s important to stop and reassess.
- Consulting a Healthcare Provider : If pain during intercourse persists, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and advice.
By following these strategies, women can help protect themselves from discomfort and injury during
What is female clitoris ?
The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva, which is the external part of the female genitalia. It plays a crucial role in female sexual arousal and pleasure. Here are some key points about the clitoris:
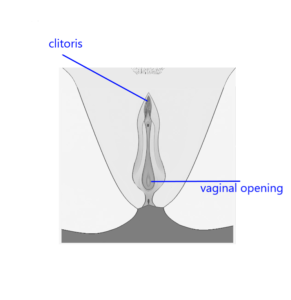
Anatomy : The clitoris is often described as having a “wishbone” shape, with a visible external part (the glans) and a larger internal structure that extends deeper into the body. The glans is typically about the size of a pea and is covered by a fold of skin called the clitoral hood.
Function : The primary function of the clitoris is to provide sexual pleasure. It contains a high concentration of nerve endings—estimated to be around 8,000—making it one of the most sensitive areas of the human body.
Erectile Tissue: Similar to the penis, the clitoris contains erectile tissue that can fill with blood and become engorged during sexual arousal, leading to increased sensitivity and pleasure.
Role in Sexual Response : Stimulation of the clitoris can lead to sexual arousal, orgasm, and overall sexual satisfaction. Many women find clitoral stimulation to be essential for achieving orgasm.
Cultural and Historical Context : The clitoris has often been misunderstood or overlooked in discussions about female sexuality. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of its importance in sexual health and pleasure.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the clitoris is essential for promoting sexual health and well-being among
What is the cervix in vagina ?
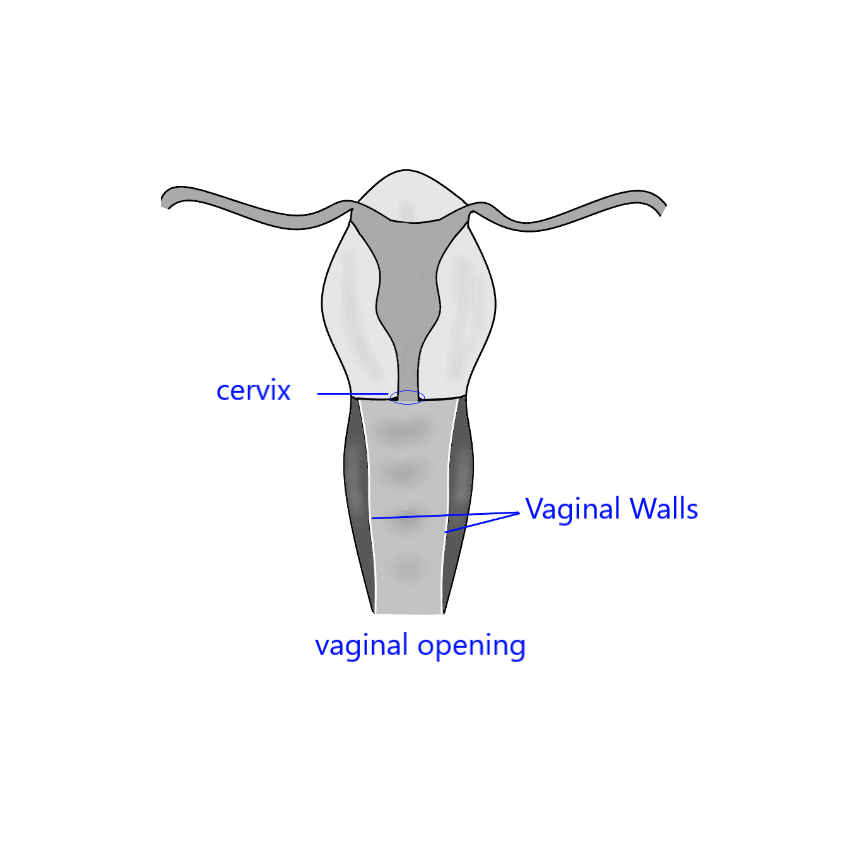
The cervix is a dynamic sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity.It is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous.
The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman’s life cycle. For example, during the fertile years of a woman’s reproductive cycle, females tend to have a larger cervix in comparison to postmenopausal females; Similarly, women who have had children have a larger cervix than women who have not had children.
In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the internal os and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the external os, while between is the conduit of the cervix, commonly referred to as the cervical canal.
How deep is the cervix in vagina ?
The cervix is a dynamic sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity.
The cervix is typically located about 3 to 6 inches (7.5 to 15 cm) inside the vagina from the vaginal opening. This distance can vary depending on factors like age, childbirth history, and individual anatomy.
What are the most pleasurable points of vagina ?
Understanding the pleasure points within the female vagina can enhance sexual experiences and increase the likelihood of achieving orgasm. According to recent studies and expert opinions, there are several key pleasure zones that have been identified:
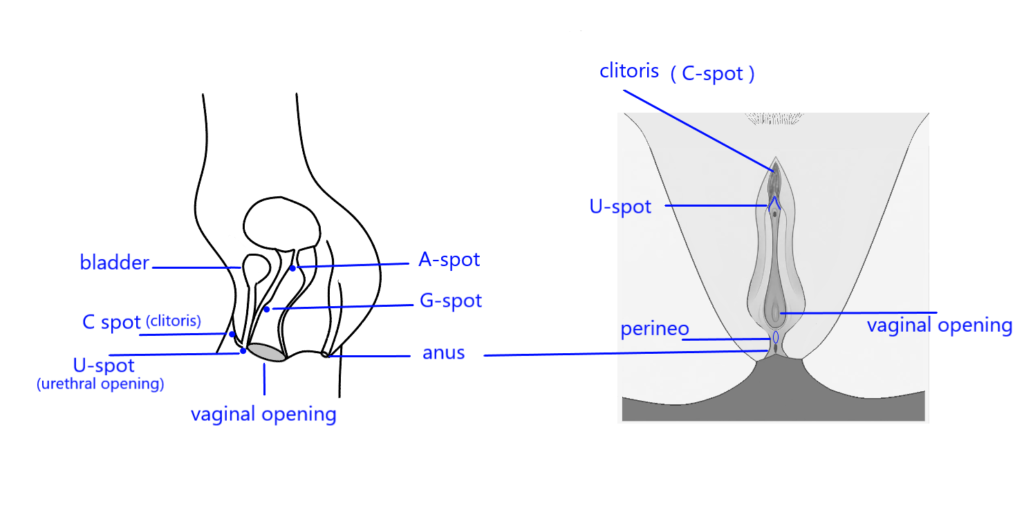
- Vaginal Entryway
The vaginal entryway is often referred to as “using the front door.” This area includes the first inch or so inside the vaginal canal, where many nerve endings are concentrated. Stimulation in this region can be particularly pleasurable for many individuals. Techniques such as shallow penetration with fingers or toys can be effective in exploring this area. - G-Spot
The G-spot, also known as the Gräfenberg spot, is located about two to three inches deep on the front wall of the vagina. It is often described as a sensitive area that can lead to intense pleasure and even orgasm when stimulated correctly. To find it, one might use a “come hither” motion with their fingers while applying gentle pressure from above with their other hand on the lower abdomen. - Clitoris
Although technically outside of the vaginal canal, the clitoris is considered one of the most important erogenous zones for many individuals with vaginas. It contains a high concentration of nerve endings and is crucial for achieving orgasm for most women. Stimulation of this area—whether through direct contact or indirectly via vaginal penetration—can significantly enhance sexual pleasure. - A-Spot (Anterior Fornix)
The A-spot is located deeper inside the vagina, near the cervix, and may provide pleasurable sensations when stimulated. Some individuals report that stimulation in this area can lead to heightened arousal and intense orgasms. - U-Spot (Urethral Sponge)
Located around the urethra, this area can also be sensitive to stimulation and may contribute to sexual pleasure for some individuals. - Perineum
While not part of the vaginal canal itself, stimulating the perineum (the area between the vagina and anus) can enhance overall sexual pleasure and arousal.
Each individual may respond differently to stimulation in these areas; therefore, exploration and communication with partners are essential for discovering what feels best.
What is the average size a vagina
The size of the female vagina can vary significantly among individuals, and there is no “normal” size. However, some general information can be provided:
Length: The average length of an unaroused vagina is about 7.5 to 10 cm (3 to 4 inches). When aroused, it can expand to accommodate penetration, often increasing in length and width.
Width: The width of the vagina can also vary, but it typically ranges from about 2.5 to 3.5 cm (1 to 1.5 inches) when unaroused.
It’s important to note that the vagina is a highly elastic organ, capable of stretching and accommodating various sizes. Factors such as age, hormonal changes, and individual anatomy can influence these measurements.
Why does a long penis hurt some females?
A very long penis may hit the cervix during thrusting, which can be painful. If vagina is not wet enough, penis with extra girth may tear delicate vaginal tissues if females don’t use enough lubricant.
Can a human penis tore or hurt a female vagina ?
Yes, it is possible for a human penis to cause discomfort, tearing, or injury to the female vagina, although such occurrences are relatively rare. Here are some factors that can contribute to this:
- Lack of Lubrication : Insufficient lubrication during sexual intercourse can lead to friction, which may cause irritation or tearing of the vaginal walls. This is particularly common if the woman is not adequately aroused or if there is a lack of natural lubrication.
- Forceful or Aggressive Intercourse : Engaging in very forceful or aggressive sexual activity can increase the risk of injury. If the thrusting is too hard or fast, it may lead to discomfort or tearing.
- Vaginal Dryness : Conditions that cause vaginal dryness, such as hormonal changes (e.g., menopause), certain medications, or medical conditions, can make the vaginal tissues more susceptible to injury.
- Infections or Medical Conditions : Certain infections (like yeast infections or sexually transmitted infections) or medical conditions (such as vaginismus or vulvodynia) can make the vaginal tissues more sensitive and prone to injury.
- Anatomical Variations : Individual anatomical differences can also play a role. For example, some women may have a narrower vaginal canal, which could increase the risk of discomfort or tearing during penetration.
- Hymenal Tissue : In some cases, if a woman is a virgin or has not engaged in penetrative intercourse before, the hymen (a thin membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening) may stretch or tear, which can cause discomfort or bleeding.

What are the best places to lick vagina?
Understanding the pleasure points within the female vagina can enhance sexual experiences and increase the likelihood of achieving orgasm.The most recognized pleasure points within the female vagina include:
Vaginal Entryway, Clitoris, Perineum
Female Pubic Hair
Definition and Purpose
Female pubic hair refers to the hair that grows in the genital area of women, typically starting during puberty. This hair serves several important functions:
- Protection: Pubic hair acts as a barrier, protecting sensitive skin from friction during sexual activity and preventing irritation.
- Hygiene: It helps trap sweat, oil, and bacteria, which can contribute to body odor but also plays a role in maintaining cleanliness by preventing dirt and germs from entering the vaginal area.
- Pheromone Storage: The hair traps pheromones produced by apocrine glands, which may play a role in sexual attraction.

Types of Female Pubic Hair
Female pubic hair can vary widely in terms of texture, thickness, and growth patterns. Here are some common characteristics:
- Texture: Pubic hair can be curly, wavy, or straight. Curly hair is more common and can help reduce friction.
- Thickness: Some women have thick, coarse pubic hair while others may have finer strands. The density can vary significantly among individuals.
- Color: The color of pubic hair may differ from the hair on the head; it can be darker or lighter depending on genetics.
Grooming Styles
Women often choose different grooming styles for their pubic hair based on personal preference or societal trends. Some popular styles include:
- Natural Bush: Allowing the pubic hair to grow freely without any trimming or shaving.
- Bikini Trim: Removing only the visible hairs that would protrude from a bikini bottom.
- Brazilian Wax: Removing all or most of the pubic hair for a completely bare look.
- Landing Strip: Leaving a thin strip of hair while removing most of the surrounding hairs.
Trends and Cultural Perspectives
The perception and grooming of female pubic hair have evolved over time:
- In recent years, there has been a trend towards embracing natural growth with many women opting not to remove their pubic hair at all.
- Conversely, some women still prefer complete removal due to personal comfort or aesthetic preferences influenced by cultural norms.
What are the benefits of pubic hair for women?
Pubic hair serves several purposes for females. It provides a natural barrier that helps protect against bacteria and other pathogens, reducing the risk of infections. It also reduces friction during physical activities, which can help prevent skin irritation. Additionally, pubic hair can play a role in regulating body temperature by trapping heat and moisture. It’s a natural part of the body that has evolved for these protective and functional reasons.
Should i remove my pubic hair
That’s a personal choice, and there’s no right or wrong answer. Some people prefer to remove it for aesthetic reasons, comfort, or hygiene, while others choose to keep it for its protective benefits. It’s important to do what feels right for you and your body. If you decide to remove it, make sure to do so safely to avoid irritation or infection. If you’re unsure, you might want to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.