Sperm Health and Structure
Sperm Cell
Sperm cells are the male reproductive cells, also known as spermatozoa, produced in the male reproductive system. They play a crucial role in sexual reproduction by fertilizing female egg cells (ova) to create a new organism. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what male sperm is:
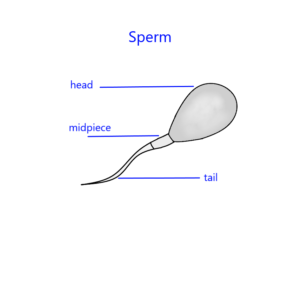
Structure of Sperm
Sperm cells have a unique structure that consists of three main parts:
- Head:
- The head contains the nucleus, which houses the genetic material (DNA). In humans, this includes 23 chromosomes, which combine with the 23 chromosomes from the egg during fertilization to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes.
- The head is covered by a cap called the acrosome, which contains enzymes necessary for penetrating the outer layer of an egg.
- Midpiece:
- This section contains mitochondria that provide energy for the sperm’s movement. The energy produced is essential for propelling the sperm towards the egg.
- Tail (Flagellum):
- The tail is responsible for the motility of the sperm. It moves in a whip-like manner to propel the sperm through fluid environments toward the egg.
Production and Lifespan of sperm
- Spermatogenesis: Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules within the testicles through a process called spermatogenesis. This process begins at puberty and continues throughout a male’s life.
- Quantity: Males typically produce millions of sperm daily; an average ejaculation can contain between 15 million to over 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen.
- Lifespan: Once ejaculated, sperm can live up to five days within the female reproductive tract but only about an hour outside of it under normal room temperature conditions.
Main Function of the sperm
The primary function of sperm is to fertilize an ovum (egg cell). During sexual intercourse or assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF), sperm travel through the female reproductive system to reach and penetrate an egg, leading to conception.
Factors Affecting Sperm Health
Several factors can influence sperm quality and quantity, including:
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and obesity can negatively impact sperm health.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and heat can also affect fertility.
- Medical Conditions: Issues such as varicoceles (swollen veins in the scrotum), infections, hormonal imbalances, and genetic disorders can impair sperm production or function.
In summary, male sperm are specialized cells essential for reproduction, characterized by their unique structure and function aimed at achieving fertilization with female eggs.
When do male stop producing sperm ?
Male fertility generally decreases with age, but there isn’t a specific age at which a man becomes entirely unable to father a child. Factors such as sperm quality, health conditions, and lifestyle choices can affect fertility.
Typically, men experience a gradual decline in fertility starting in their 40s and 50s. However, there have been cases of men fathering children well into their 70s and even 80s. While the quantity and motility of sperm may decrease with age, it’s not entirely uncommon for older men to still be able to conceive.
- FAQ
What are sperm?
Sperm are male reproductive cells produced in the testes that are necessary for fertilizing a female’s egg.
How many sperm does a man produce in a lifetime?
A man can produce billions of sperm throughout his life, with estimates suggesting around 1,500 sperm per second after puberty.
What is the average sperm count per ejaculation?
The average sperm count is typically between 40 million and 300 million sperm per milliliter of semen.
What factors can affect sperm production?
Factors such as age, lifestyle choices (like smoking and alcohol consumption), environmental toxins, and health conditions can all impact sperm production.
How long do sperm live inside the female reproductive system?
Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days under optimal conditions, particularly during the fertile window of the menstrual cycle.
What is considered a low sperm count?
A low sperm count is defined as fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen, which may affect fertility potential.
Can men run out of sperm?
No, men do not run out of sperm; their bodies continuously produce new sperm throughout their lives.
What is the role of testosterone in sperm production?
Testosterone plays a crucial role in stimulating spermatogenesis (the process of producing sperm) within the testes.
How does temperature affect sperm health?
Sperm production requires cooler temperatures than normal body temperature; excessive heat from hot baths or tight clothing can negatively impact spermatogenesis.
What is semen made of?
Semen consists of sperm cells along with fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands that nourish and transport the sperm.
How fast can sperm swim?
.Sperm can swim at speeds up to approximately 28 miles per hour (45 kilometers per hour) when they are first ejaculated but generally move slower once inside the female reproductive tract.
What tests are used to assess male fertility?
A semen analysis is commonly used to evaluate male fertility by measuring parameters like volume, concentration, motility (movement), and morphology (shape) of the sperm cells.
Can diet influence sperm quality?
Yes, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins (like Vitamin C and D), and healthy fats can improve overall sperm quality and motility.
Is it possible for men to have no viable sperm?
Yes, this condition is known as azoospermia; it can be caused by various factors including genetic issues or blockages in the reproductive tract.
How does age affect male fertility?
As men age, especially past age 40, there may be declines in testosterone levels and overall semen quality which could impact fertility rates and increase risks for genetic abnormalities in offspring.
Can stress affect male fertility?
Yes, high levels of stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may negatively impact both testosterone levels and overall fertility potential in men.
Are there any medications that affect sperm production?
Certain medications such as anabolic steroids or some cancer treatments (like chemotherapy) can adversely affect hormone levels and reduce or eliminate viable sperm production temporarily or permanently depending on treatment type and duration.
What lifestyle changes can improve male fertility?
Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, managing stress levels, and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins can enhance male fertility outcomes significantly.
Can varicocele affect fertility?
Yes, varicocele—enlarged veins within the scrotum—can lead to increased temperature around the testes which may impair spermatogenesis resulting in lower quality or quantity of produced sperm cells.
Is there a link between obesity and low testosterone levels affecting fertility?
Yes, obesity has been associated with lower testosterone levels which may contribute to reduced libido as well as decreased quality and quantity of produced sperm cells impacting overall fertility potential in men who are overweight or obese compared to those with healthier weights.
Do all men produce healthy-looking sperms?
Not all men produce healthy-looking sperm. Sperm quality can vary greatly depending on several factors like age, lifestyle, health conditions, and even environmental exposures.
Can supplements help boost male fertility?
Yes, certain supplements may help boost male fertility by improving sperm count, motility, and overall quality. Some commonly recommended supplements include: Vitamin C, D , Zinc , Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these can improve sperm concentration and quality.
When should someone seek professional help regarding concerns about their reproductive health?
If experiencing persistent difficulties achieving pregnancy after one year unprotected intercourse , guidance from qualified specialists recommended.
What is male ejaculation?
Male ejaculation is the release of semen from the penis during sexual arousal.
How does ejaculation happen?
Ejaculation happens when muscles around the reproductive organs contract, pushing semen out through the urethra.
Can a man ejaculate without having an orgasm?
Yes, a man can ejaculate without experiencing an orgasm.
How much semen do men usually ejaculate?
Men typically ejaculate about 5 milliliters of semen, which is roughly one teaspoon.
How many sperm are in an average ejaculation?
An average ejaculation contains about 100 million sperm.
What factors affect how quickly a man ejaculates?
Factors include physical health, emotional state, level of arousal, and experience with sexual activity.
Is there a normal number of spurts during ejaculation?
No, some men may have one spurt while others may have multiple spurts during ejaculation.
Does age affect the amount of semen produced?
Yes, as men age, the amount of semen they produce may decrease.
What is premature ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation occurs when a man ejaculates sooner than he or his partner would like during sexual activity.
What causes premature ejaculation?
Causes can include anxiety, stress, relationship issues, or past experiences related to sex.
Can lifestyle choices impact ejaculation timing?
Yes, factors like alcohol use, drug use, and overall health can influence how quickly a man ejaculates.
Are there treatments for premature ejaculation?
Yes, treatments can include behavioral techniques, counseling, and medications like SSRIs or topical anesthetics.
What are Kegel exercises and how do they help with ejaculation control?
Kegel exercises strengthen pelvic floor muscles and can help improve control over ejaculation timing during sex.
Can women also experience ejaculation?
Yes! Some women can ejaculate as well; however, the process is different from male ejaculation.
How often should men ejaculate for good health?
There isn’t a specific frequency; it varies by individual preference and health needs but regular sexual activity is generally considered healthy for men.
Can certain medications affect ejaculation?
Yes, some medications such as antidepressants can delay or speed up the process of ejaculation depending on their effects on the body’s systems involved in sexual function.
Is it normal for men to worry about their performance during sex?
Yes, many men experience anxiety about their performance which can impact their ability to control ejaculation timing during sex activities.
Can psychological factors contribute to delayed or premature ejaculation?
Yes, Stress and anxiety are significant contributors to both conditions affecting how quickly or slowly a man ejaculates
Is there any link between masturbation frequency and problems with ejaculation?
Masturbation habits may influence how quickly someone ejaculates; frequent quick releases might condition faster responses during partnered sex.
Can practicing relaxation techniques help with controlling ejaculation?
Yes! Techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness can reduce anxiety levels that might lead to premature or delayed responses.