Female breasts
This webpage provides clear and simple information about female breasts. It explains their structure, function, and unique features in an easy-to-understand way for learning and exploration.
Female Breast Growth with Age
Introduction to Breast Development
Breast development is a significant aspect of female puberty, typically beginning between the ages of 8 and 13. The initial stage is marked by the formation of breast buds, which are small swellings under the nipple. This process is driven by hormonal changes, particularly the increase in estrogen produced by the ovaries.
Stages of Development
- Early Development (Ages 8-13): The first visible sign of breast growth occurs as breast buds form. During this time, girls may experience tenderness and soreness as their breasts begin to grow.
- Continued Growth (Ages 14-17): As puberty progresses, breasts continue to develop and become rounder and fuller. The areola may darken and enlarge, while the nipples may become more pronounced. By age 17, most girls will have fully developed breasts; however, some may continue to grow into their early twenties.
- Post-Puberty Changes (Ages 18+): After reaching full development, breast size can still fluctuate due to factors such as weight gain or loss, hormonal changes during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and aging.

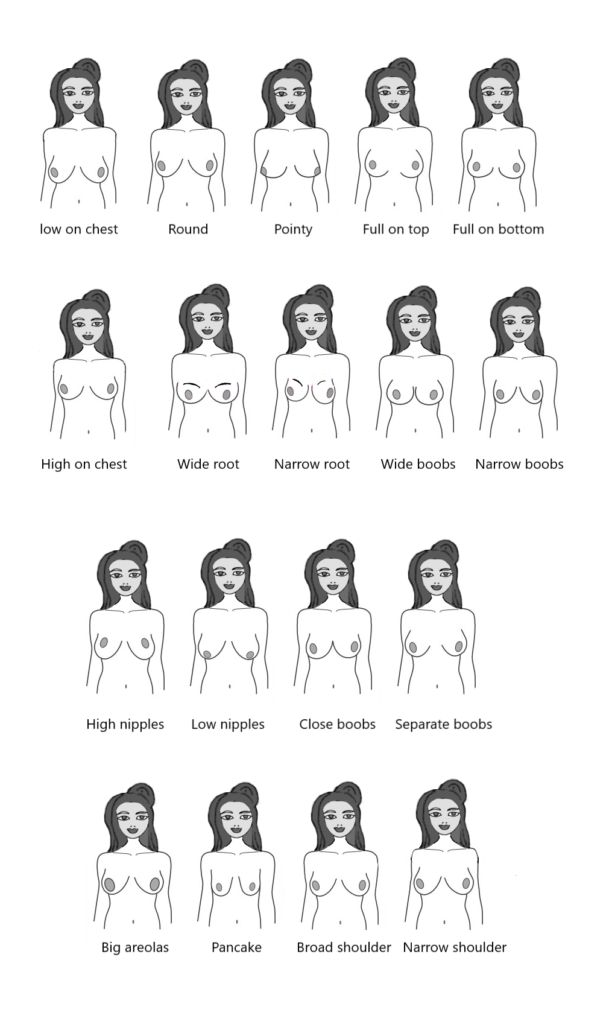
What are the main types of female breast?
Breasts come in many shapes and sizes, and each type is unique. Knowing about these different breast types can help women feel more comfortable and confident in their bodies. Here are some common types of female breasts:
1. Round Breasts
Round breasts are equally full at the top and bottom. They have a smooth, rounded shape that many people consider classic.
2. Teardrop Breasts
Teardrop breasts are fuller at the bottom and slightly less full at the top, resembling the shape of a teardrop. This shape gives a natural look.
3. Bell-Shaped Breasts
Bell-shaped breasts are narrow at the top and wider at the bottom, similar to a bell. This type is often seen in women with larger breasts.
4. Asymmetrical Breasts
Asymmetrical breasts occur when one breast is noticeably larger or shaped differently than the other. It’s common for women to have some degree of asymmetry.
5. East-West Breasts
East-West breasts have nipples that point outward, away from the center of the chest. This shape creates more space between the breasts.
6. Side-Set Breasts
Side-set breasts are further apart from each other, with more space between them compared to other types. The nipples usually point forward.
7. Relaxed Breasts
Relaxed breasts have softer tissue and may sag slightly, especially when not supported by a bra. The nipples may also point downward.
Conclusion
Every woman has her own unique breast shape, which is completely normal and beautiful. Understanding these types can help promote body positivity and self-acceptance among women.
Why do females have breasts?
Breasts in females serve several biological and evolutionary purposes:
- Lactation : The primary function of breasts is to produce milk for feeding infants. This is crucial for the survival and nutrition of newborns, especially in the early stages of life.
- Sexual Selection : Breasts are often considered secondary sexual characteristics. They can play a role in sexual attraction and mate selection, signaling fertility and health to potential partners.
- Hormonal Influence : Breast development is influenced by hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, which increase during puberty and pregnancy. This development prepares the body for potential breastfeeding.
- Fat Storage : Breasts are composed of glandular tissue and fat. The fat can serve as an energy reserve, which may be beneficial during periods of lactation when energy demands are high.
- Cultural and Social Factors : Beyond biological functions, breasts have significant cultural and social meanings in many societies, influencing fashion, art, and personal identity.
Overall, the presence of breasts in females is a complex interplay of biological, evolutionary, and social factors.
Why do women usually have two breasts?
Females typically have two breasts due to several evolutionary and biological reasons:
- Symmetry and Balance : Having two breasts provides symmetry, which is often associated with health and genetic fitness. Symmetry can be an important factor in sexual selection, as it may signal good health and reproductive capability.
- Lactation Efficiency : Two breasts allow for the possibility of feeding two infants simultaneously, which can be advantageous in terms of survival and reproductive success. This is particularly relevant in species where multiple births can occur.
- Evolutionary Adaptation : The development of two breasts may be an evolutionary adaptation that has persisted because it offers advantages in terms of offspring survival and maternal investment.
- Hormonal Regulation : The development of breasts is regulated by hormones, and the presence of two breasts is a result of the biological processes that occur during puberty and pregnancy, influenced by hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Genetic Factors : The genetic blueprint for humans includes the development of two breasts as a standard trait for females, which is consistent across many mammalian species.
Overall, the presence of two breasts in females is a result of evolutionary pressures, biological functions, and genetic factors
What influences female breast size?
Breast size varies significantly among individuals and is primarily determined by genetics. Additionally, body fat plays a role since breasts contain adipose tissue; thus, weight changes can affect breast size.
Conclusion
Understanding the stages of breast development helps demystify this natural process that many young women experience during puberty and beyond.

How can i increase my breast size ?
There isn’t a specific exercise or system that can significantly increase breast size, as breast tissue is primarily made up of fat and glandular tissue, not muscle. However, certain exercises can help improve the overall appearance and firmness of the chest area by strengthening the pectoral muscles underneath the breasts. Some exercises that can help tone and strengthen the chest muscles include:
- Push-ups
- Chest presses
- Chest flies
Remember, everyone’s body is unique, and it’s important to embrace and appreciate your natural shape.
When do female breasts stop growing ?
Breast development begins between the ages of 8 and 13. Female breasts typically stop growing by the late teens to early twenties. However, this can vary from person to person. Factors like genetics, hormonal changes, and overall health can influence breast development.
why my breasts are so small , i am 20
Breast size varies greatly among individuals and is influenced by factors like genetics, hormones, and overall body composition. It’s important to remember that there’s no “normal” or “ideal” breast size—everyone’s body is unique and beautiful in its own way.
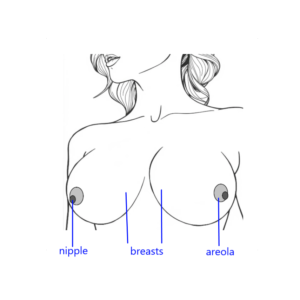
What are areolas on female breasts ?
Areolas are the circular areas of darker skin surrounding the nipples on the breasts. They vary greatly in size, shape, and color among individuals. The diameter of areolas can range from about 1 inch (2.5 cm) to several inches (up to around 6 inches or 15 cm) across. Factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, age, and pregnancy can all influence the size and appearance of the areolas.
What causes breast size differences between individuals?
Breast size differences can be attributed to a variety of factors including genetics, hormonal levels, body weight, and age. Hormonal changes during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause can also influence breast size. Genetics plays a significant role in determining the overall shape and size of breasts.
Is it normal for one breast to be larger than the other?
Yes, it is completely normal for one breast to be larger than the other. Many women experience some asymmetry in breast size, which can vary throughout life due to hormonal changes or weight fluctuations.
How do breasts change with age?
As women age, particularly after menopause, breasts undergo several changes including a decrease in glandular tissue and an increase in fatty tissue. This change can lead to less firmness and more sagging due to gravity and loss of collagen in the skin.
What is the most sensitive part of a female's breasts ?
The skin of the superior quadrant is the most sensitive part of the breast, the areola is less sensitive, and the nipples are the least sensitive part. Sensitivity can vary from person to person, and other parts of the breasts may also be sensitive for some individuals.

How to Lift Your Breasts at Home Easily?
Lifting your breasts at home can be achieved through a combination of exercises, proper nutrition, and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
- Chest Exercises
While breasts themselves do not contain muscles, the underlying pectoral muscles can be strengthened to improve the overall appearance of your chest. Here are some effective exercises you can perform at home:
Chest Press,Chest Fly,Push Ups
- Maintain Good Posture
Good posture plays a crucial role in how lifted your breasts appear. Practice standing and sitting up straight with shoulders back and down. This helps distribute weight evenly and reduces strain on breast tissue.
- Wear Supportive Bras
Investing in well-fitted bras that provide adequate support is essential. A good bra can help lift and shape the breasts, reducing sagging over time. Make sure to get re-fitted if you experience weight changes.
- Healthy Diet and Hydration
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports skin elasticity. Focus on foods high in antioxidants (like fruits and vegetables), healthy fats (such as avocados and nuts), and proteins (like lean meats). Staying hydrated by drinking enough water also helps maintain skin health.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Sun Exposure
Smoking can damage skin elasticity, leading to sagging breasts over time. Additionally, excessive sun exposure can break down collagen in the skin; therefore, using sunscreen when outdoors is advisable.
- Consider Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy weight is important since being overweight can contribute to sagging due to added pressure on breast tissue. If you experience significant weight loss, it may also affect breast shape.
By incorporating these exercises into your routine along with maintaining good posture, wearing supportive bras, eating healthily, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking, limiting sun exposure, and managing weight effectively, you can work towards achieving a lifted appearance for your breasts at home.
Can diet affect breast health?
Yes, certain dietary choices can impact overall health including breast health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes may help reduce cancer risk and promote general well-being of breast tissue. Foods high in phytosterols have been shown to inhibit tumor development according to some studies.
Do bras prevent sagging?
While wearing bras can provide support and comfort, they do not prevent sagging over time as sagging is primarily caused by aging and gravity affecting connective tissues within the breasts. A supportive sports bra may help during physical activities but does not stop natural aging processes from occurring.
What Happens to Females When Males Kiss Their Breasts?
When a male kisses a female’s breasts, several physiological and psychological responses can occur. These reactions can vary significantly among individuals based on personal preferences, comfort levels, and the context of the interaction.
- Physiological Responses:
- Increased Blood Flow: Kissing or stimulating the breasts can lead to increased blood flow to the area. This is due to arousal, which causes blood vessels to dilate, resulting in heightened sensitivity.
- Hormonal Changes: Physical intimacy often triggers the release of hormones such as oxytocin (the “love hormone”) and dopamine (associated with pleasure). These hormones can enhance feelings of closeness and pleasure.
- Breast Sensitivity: The breasts are sensitive areas for many women due to a high concentration of nerve endings. Kissing can stimulate these nerve endings, leading to pleasurable sensations.
- Physical Reactions: Some women may experience physical reactions such as increased heart rate, changes in breathing patterns, or even involuntary muscle contractions in response to stimulation.

- Psychological Responses:
- Emotional Connection: Kissing is often associated with intimacy and affection. A kiss on the breasts can enhance emotional bonding between partners if both feel comfortable and consenting.
- Arousal Levels: For many women, kissing on the breasts can be an erotic act that increases sexual arousal. This may lead to further intimate interactions if both parties are willing.
- Comfort and Consent: The psychological impact also heavily depends on whether the woman feels safe and respected in the situation. If she consents and enjoys the act, it can lead to positive feelings; however, if she feels uncomfortable or pressured, it may result in negative emotions.
- Individual Variability:
- It is essential to recognize that every individual has different preferences regarding physical touch. While some women may find kissing their breasts pleasurable and intimate, others might not enjoy it or might feel uncomfortable with such actions.
- Communication between partners about boundaries and preferences is crucial for ensuring that both individuals have a positive experience.
In summary, when a male kisses a female’s breasts, it can elicit various physiological responses like increased blood flow and hormonal changes alongside psychological effects such as enhanced emotional connection or arousal levels. However, individual responses will vary widely based on personal comfort levels and consent.
Why breast pain before periods?
Breast pain before menstruation is often due to hormonal fluctuations that occur during the menstrual cycle. This condition, known as cyclical mastalgia, is common and usually resolves after menstruation begins.
- FAQ
When do breasts typically start developing in girls?
Breasts usually start developing around ages 9 to 10, but this can vary based on individual factors such as genetics and ethnicity.
What are breasts primarily made of?
Breasts are primarily composed of glandular tissue, adipose (fat) tissue, and connective tissue.
Is it normal for one breast to be larger than the other?
Yes, it is completely normal for one breast to be slightly larger than the other; most women experience some degree of asymmetry.
Do breasts continue to grow after puberty?
Breast growth typically continues until around age 18, but changes can occur throughout a woman’s life due to hormonal fluctuations, weight changes, and pregnancy.
Can birth control pills affect breast size?
Birth control pills may cause temporary breast swelling or tenderness due to hormonal changes, but they do not significantly increase breast size long-term.
What causes breast tenderness before menstruation?
Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can lead to breast tenderness due to increased blood flow and swelling in the breast tissue.
Are nipple hairs normal?
Yes, having fine hair around the nipples is common and generally not a cause for concern unless there is a sudden change in hair density or texture.
How often should women perform self-breast exams?
Women should perform self-breast exams monthly to become familiar with their normal breast tissue and detect any changes early on.
What does it mean if a lump is found in the breast?
Finding a lump in the breast can be concerning, but it doesn’t always mean something serious. Many breast lumps are benign (non-cancerous) and can result from various causes, such as hormonal changes, cysts, or fibroadenomas
Can dense breasts increase cancer risk?
Yes, having dense breasts can increase the risk of developing breast cancer and make it more difficult for radiologists to detect tumors on mammograms.
what is nipple piercings?
Nipple piercings involve inserting a piece of jewelry, such as a barbell or ring, through the nipple. It’s a form of body modification and self-expression that has cultural, aesthetic, and sometimes personal significance for those who choose it.
Is it safe to get nipple piercings?
Nipple piercings can be safe if performed by a qualified professional using sterile techniques; however, there are risks such as infection or allergic reactions that should be considered beforehand.
Do all women experience changes in their breasts during pregnancy?
Yes, most women will notice significant changes in their breasts during pregnancy due to hormonal shifts preparing for lactation; these changes include increased size and sensitivity.
Can exercise improve the appearance of breasts?
While exercise cannot directly lift or change breast tissue since they are primarily made of fat, strengthening chest muscles underneath can enhance overall appearance and firmness of the bust area.
How does breastfeeding affect breast shape after weaning?
Breastfeeding can temporarily change the shape and size of breasts; after weaning, some women may notice sagging or loss of volume due to stretched skin and tissues during lactation periods.
Are there any non-cancerous conditions that affect breasts?
Yes, conditions like fibrocystic changes (lumpy or painful areas), cysts (fluid-filled sacs), and mastitis (inflammation) are common non-cancerous issues affecting women’s breasts at various stages of life.
Can weight loss impact breast size significantly?
Yes, weight loss often leads to reduced fat deposits in the breasts which may result in decreased size; however, individual experiences vary based on body composition and genetic factors influencing fat distribution patterns across different body areas including the bustline itself!
What role do hormones play in breast health?
Hormones such as estrogen influence development throughout puberty & menstrual cycles while also affecting conditions like fibrocystic disease & even cancers later on—hormonal balance remains key!
How does aging affect women’s breasts?
Aging brings natural changes to women’s breasts due to hormonal shifts, particularly the decline in estrogen levels during menopause. This can lead to a loss of fat, tissue, and mammary glands, causing the breasts to become smaller, less full, and less firm. The skin and connective tissue also lose elasticity, which can result in sagging
Are there any myths surrounding bra usage?
Common myths suggest bras prevent sagging—however research indicates that wearing/not wearing them doesn’t significantly impact long-term sagging effects—individual comfort matters most!
Can stress impact my breasts?
Stress affects hormone levels which might lead towards tenderness/swelling among other physical manifestations—managing stress through relaxation techniques/exercise helps maintain overall well-being including your bustline!
What is breast milk made of?
Breast milk contains water, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and antibodies
Why is breast milk important for newborns?
It provides essential nutrients and antibodies that help protect babies from infections and diseases.
Can breast milk change over time?
Yes, its composition adapts to meet the baby’s changing nutritional needs as they grow.
What is colostrum?
Colostrum is the first milk produced after birth, rich in antibodies and nutrients.
How long can breast milk be stored?
Freshly expressed milk can be stored in the fridge for up to 4 days or frozen for 6-12 months.
Does breast milk help with immunity?
Absolutely! It contains antibodies that strengthen the baby’s immune system.
Can breast milk vary between mothers?
Yes, factors like diet, health, and environment can influence its composition.
Is breastfeeding beneficial for mothers?
Yes, it can reduce the risk of certain cancers and help with postpartum recovery.
Can breast milk be donated?
Yes, milk banks accept donations to help babies in need, especially preemies.
What are the signs of a good milk supply?
A baby gaining weight and having regular wet diapers are good indicators.
Can stress affect milk production?
Yes, stress can impact the let-down reflex and milk supply.
Is breast milk lactose-free?
No, it contains lactose, which is a natural sugar.
Can breast milk be used for medical purposes?
In some cases, it’s used to treat conditions like eczema or eye infections.
What is foremilk and hindmilk?
Foremilk is the watery milk at the start of feeding, while hindmilk is richer and comes later.
Can breast milk be frozen and thawed?
Yes, but it should be thawed in the fridge or warm water, not microwaved.
is breast milk also good for adults?
Breast milk is tailored specifically for infants, providing them with the nutrients and antibodies they need. While it’s not harmful for adults to consume, there isn’t significant evidence to suggest that it offers substantial health benefits for adults compared to other available sources of nutrients like dairy or plant-based milk.